Technology Overview
Coating Technologies
We utilize a variety of coating technologies to formulate the best coating process for each type of medical devices,
taking into consideration the device geometries, coating quality, process scalability and robustness.
- Plasma treatment
- Plasma polymerization
- CVD / PECVD
- Dip coating
- Spray coating
- Spin coating
- Slot-die coating
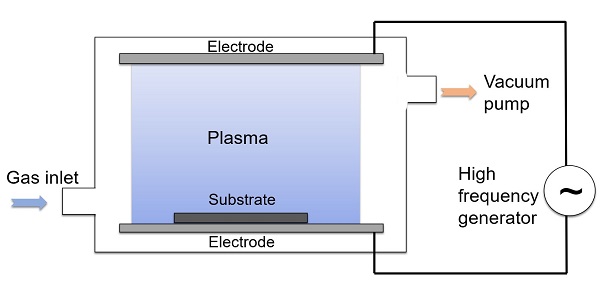
Core Technology - Plasma Assisted Polymer Coatings
We use a proprietary plasma assisted polymer coating technology (plasma polymerization, PECVD) that produces highly customized,
fully functional surfaces for a variety of applications. This innovative process uses the fourth
state of matter (plasma) to create a polymer coating on the surface of various materials, resulting
in pinhole free and complete device coverage. The resulting polymer coatings are customized for individual
applications to produce the desired surface characteristics.
Polymer surfaces created with the Medical Surface coating technology are:
- Covalently Bound
- Biologically inert and non-degradable
- Noncytotoxic
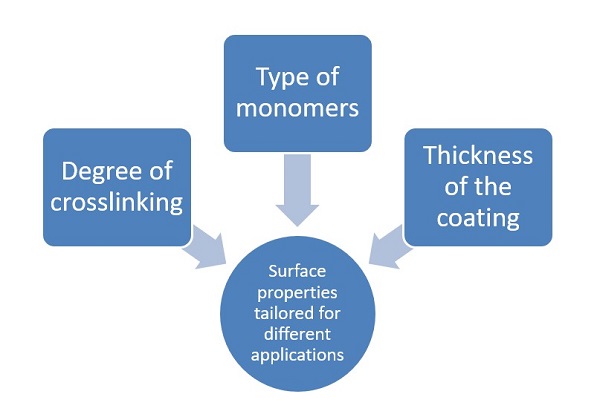
Polymer/Hydrogel Engineering Tailored for Specific Applications
The polymer/hydrogel coating can be functionalized by adding reactive functional groups to the surface. This provides a superior,
low background surface for immobilizing enzymes, antibodies and other biomolecules. Surface properties that can be engineered include:
- Hydrophilicity
- Charges
- Resistance to protein binding and cell attachment
- Permeability for small molecules
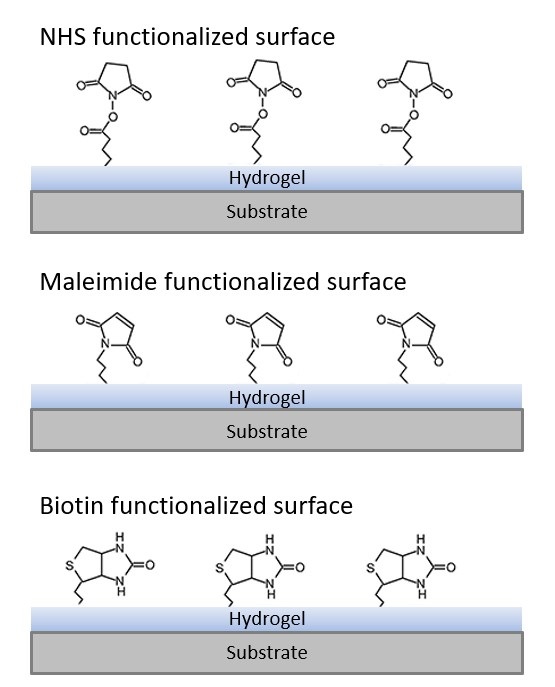
Functionalized Surface Coatings
Our innovative process allows for the engineering of the polymer/hydrogel coating,
which results in different combination of surface properties optimized for specific applications.
Examples of functional groups covalently linked to the polymer/hydrogel coating include:
- NHS group for amine immobilization
- Maleimide group for thiol immobilization
- Biotin group for streptavidin immobilization
- Ni-NTA group for poly-histidine immobilization
- Protein A for antibody immobilization
- Peptides for specific bindings
- Antibodies for antigen binding/assays
- Extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins for cell attachment